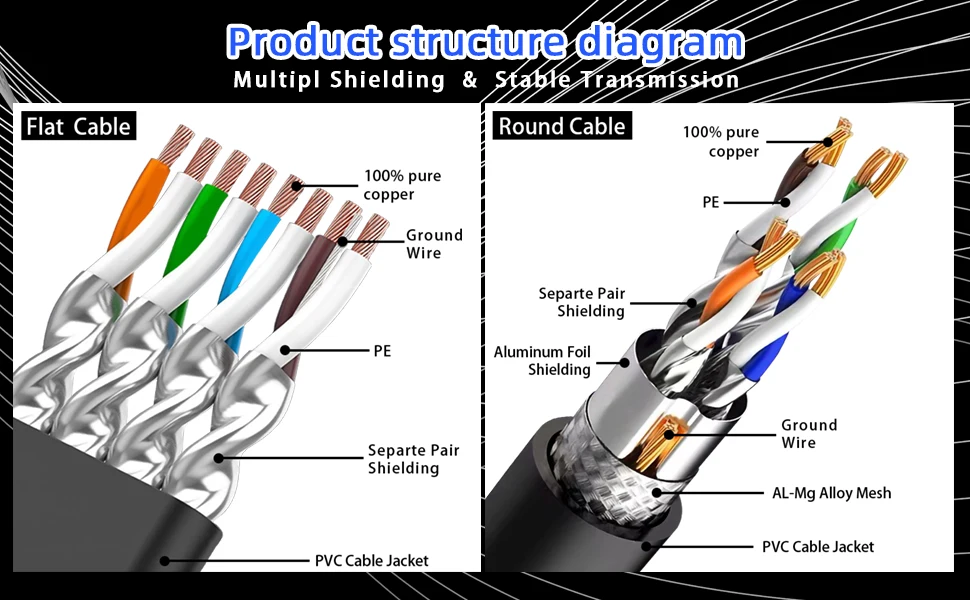
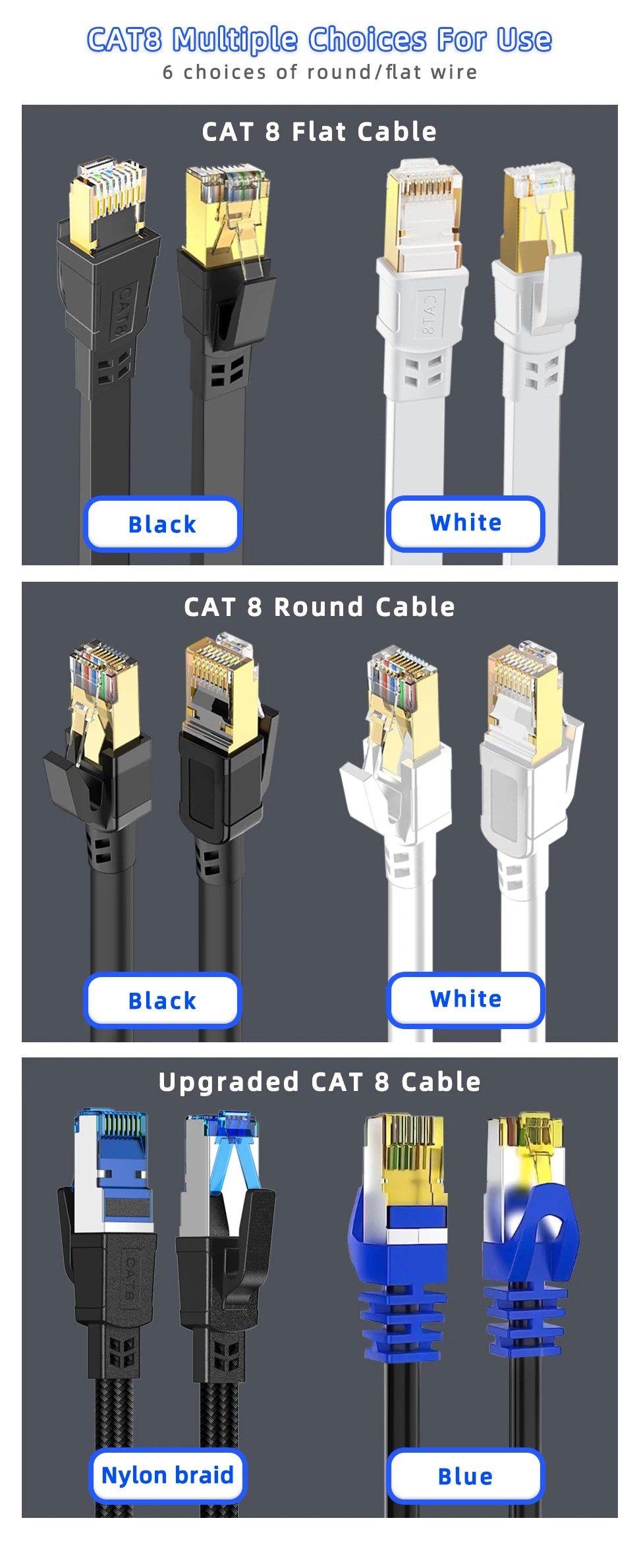
Understanding Ethernet Cables: A Comprehensive Guide
 In today's digitally connected world, Ethernet cables are the backbone of reliable network connections, playing a crucial role in how we communicate and access information. With the multitude of devices that rely on a stable internet connection—such as computers, gaming consoles, smart TVs, and even smart home devices—understanding the types of Ethernet cables available is essential for maximizing performance and ensuring optimal connectivity.
In today's digitally connected world, Ethernet cables are the backbone of reliable network connections, playing a crucial role in how we communicate and access information. With the multitude of devices that rely on a stable internet connection—such as computers, gaming consoles, smart TVs, and even smart home devices—understanding the types of Ethernet cables available is essential for maximizing performance and ensuring optimal connectivity.
Whether you are setting up a home office, upgrading your gaming rig, or enhancing your home theater experience, selecting the right Ethernet cable can make all the difference in speed and reliability. However, with various cables on the market, it can be overwhelming to know which one is best suited for your needs. In this guide, we aim to demystify Ethernet cables, exploring their different types, the unique benefits they offer, and practical tips on how to choose the correct Ethernet cable for your specific setup.
Furthermore, we will provide you with a detailed Ethernet cable installation guide to streamline your setup process, ensuring that you can enjoy uninterrupted connectivity and high-speed performance. By the end of this post, readers will not only be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about Ethernet cables but also understand their pivotal role in creating efficient and robust networking solutions in both residential and commercial environments.
Join us as we delve deeper into the world of Ethernet cables and discover how this unassuming piece of technology continues to shape our connected lives.
Understanding Ethernet Cables. What Are Ethernet Cables?
Ethernet cables are a vital component in computer networking, providing a reliable means of transmitting data between devices. They are widely used in both home and office settings to connect computers, routers, switches, and other devices to a local area network (LAN) or the internet. By utilizing twisted pairs of copper wire or fiber optics, Ethernet cables ensure a fast and efficient data transfer, making them an essential tool in modern communication.