Knives: The Essential Tools for Every Kitchen
When it comes to culinary arts, knives are not just tools; they are an extension of a chef's skills and creativity. Whether you are a novice in the kitchen or a seasoned professional, understanding knife types and their specific uses can elevate your cooking experience. In the vast realm of kitchen gadgets, selecting the best kitchen knives transcends mere preference; it's about enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety in food preparation.
In this comprehensive knife buying guide, we will delve deep into the various knife types, each uniquely designed for specific slicing, dicing, and chopping tasks. You'll gain insights into the characteristics that define quality knives and learn about essential maintenance tips to keep them in top condition. Proper care not only extends the lifespan of your knives but also ensures peak performance when you need it the most.
This blog post serves as your gateway to mastering one of the most vital aspects of cooking—your knives. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped to choose, care for, and optimize your use of these indispensable kitchen tools, turning mundane meal prep into an art form. Join us as we slice through the details and uncover everything you need to know about knives!
Types of Knives
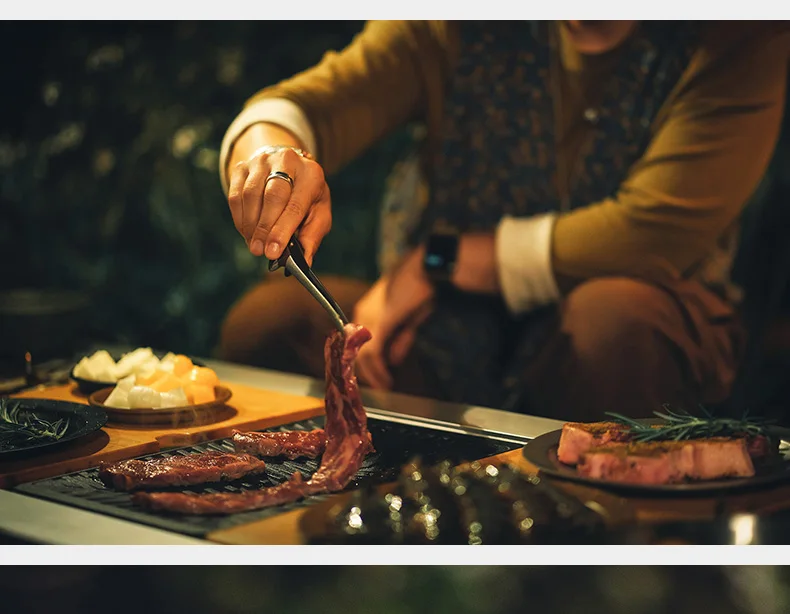
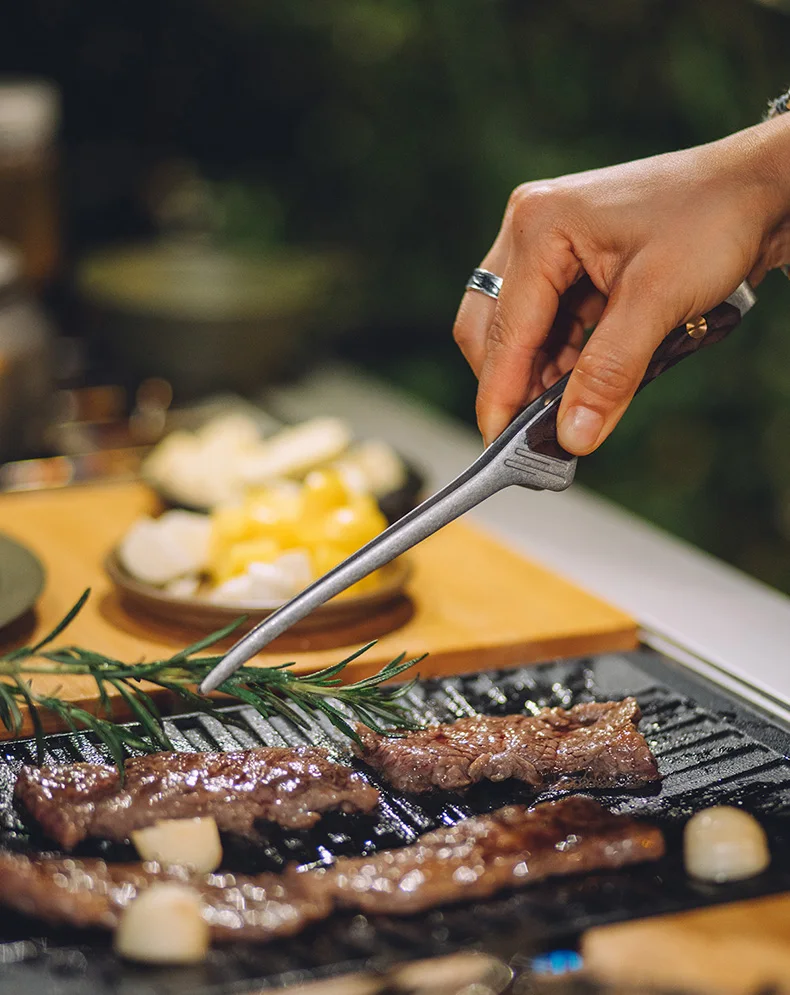
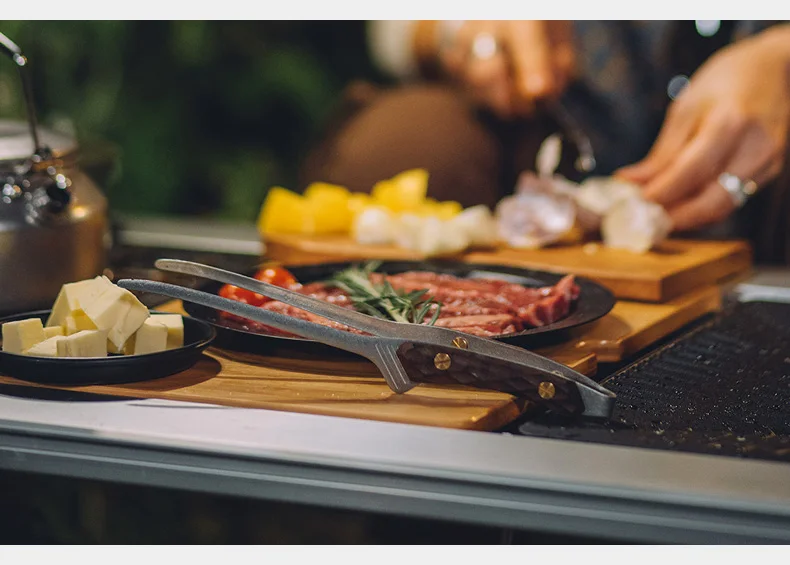
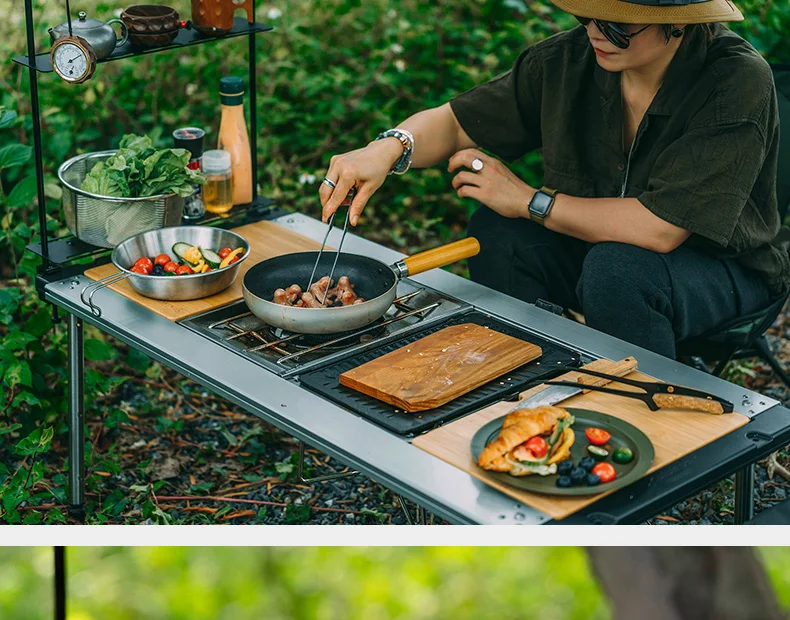
1. Kitchen Knives
When it comes to kitchen knives, these are essential tools in any cooking environment. They are specifically designed to perform various culinary tasks effectively. The core types include:
- Chef’s Knife: A versatile tool that can handle a variety of tasks such as chopping, slicing, and dicing.
- Paring Knife: Small and ideal for intricate work like peeling fruits and vegetables.
- Fillet Knife: Long and flexible, perfect for filleting fish.
- Serrated Knife: Best for cutting bread and delicate items like tomatoes.
The right kitchen knife not only boosts efficiency but also enhances safety while preparing meals. Regular knife maintenance is crucial to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
2. Pocket Knives
Pocket knives embody flexibility and convenience. These folding knives are compact and can be easily carried in a pocket, making them perfect for everyday tasks.
3. Tactical Knives
Tactical knives are specifically designed for military and self-defense purposes. With features focused on combat efficiency, they often incorporate technologies and designs that make them ideal for critical situations.
Some standard attributes include:
- Fixed Blade: Unlike folding knives, fixed blades are sturdier and can withstand more force.
- Sheath: Most tactical knives come with a sheath for safe carrying.
- Ergonomic Design: Built for comfort and ease of use during intensive activities.
These knives can be used in various scenarios, from survival situations to outdoor tasks such as camping and hiking, often being made from high-strength materials for durability.
4. Specialized Knives
Specialized knives encompass a wide array of tools that cater to specific tasks or professions. Examples include:
- Boning Knife: Used for filleting meat and poultry.
- Sushi Knife: Crafted for precise cuts in sushi preparation.
- Utility Knife: Designed for everyday tasks, often featuring a retractable blade.
These knives are expertly crafted for high functionality in their respective fields, whether it's professional cooking, crafting, or industry tasks.
5. Tips for Choosing the Best Kitchen Knives
While exploring knife types, understanding how to choose the best kitchen knives is paramount. Here are some essential tips:
- Material: Look for high-carbon stainless steel for durability.
- Weight: Opt for a weight that feels comfortable in your hand.
- Handle Type: Choose between wood, plastic, or metal based on comfort and style.
- Brand Reputation: Consider well-known brands that offer quality warranties.
Making informed decisions leads to a better kitchen experience. Regular knife maintenance, including proper cleaning and sharpening, contributes significantly to enhancing the performance and lifespan of your knives.